
Image result for cardiac muscle slide labeled cardiomyocytes Cardiac
Cardiac muscle also called the myocardium, is one of three major categories of muscles found within the human body, along with smooth muscle and skeletal muscle. Cardiac muscle, like skeletal muscle, is made up of sarcomeres that allow for contractility. However, unlike skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is under involuntary control.

cardiac muscle Definition, Function, & Structure Britannica
Cardiac muscle shows many structural and functional characteristics intermediate between skeletal and smooth muscles. Today, in this short article, I will show you the important histological features from the cardiac muscle histology slide. You will get the basic guide to learn cardiac muscle histology with real slide images and labeled diagrams.
The Heart Boundless Anatomy and Physiology
In cardiac, skeletal, and some smooth muscle tissue, contraction occurs through a phenomenon known as excitation contraction coupling (ECC). ECC describes the process of converting an electrical stimulus from the neurons into a mechanical response that facilitates muscle movement. Action potentials are the electrical stimulus that elicits the.
12.3 Types of Muscle Tissue Human Biology
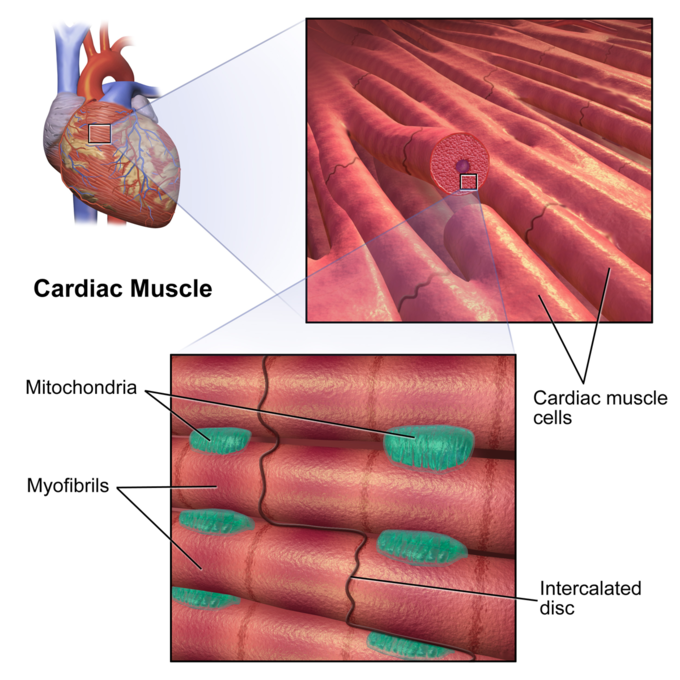
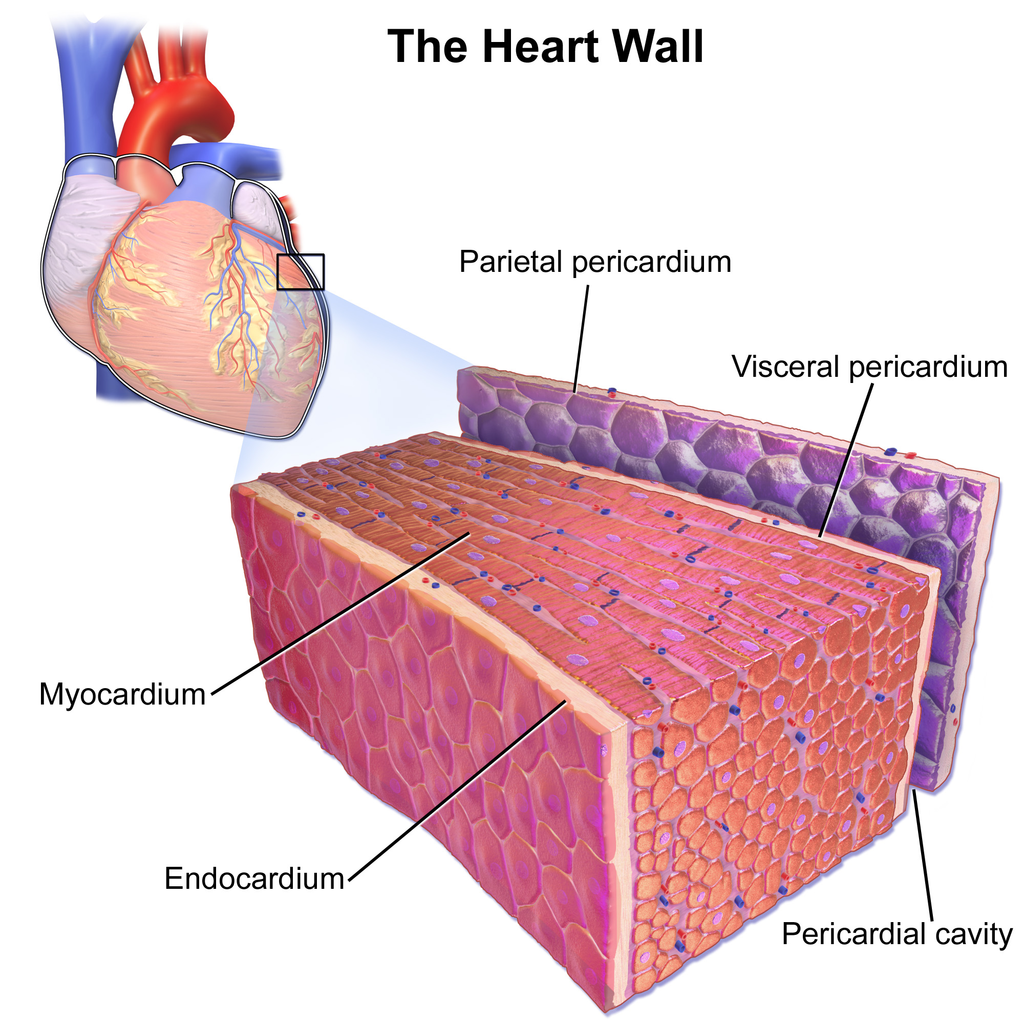
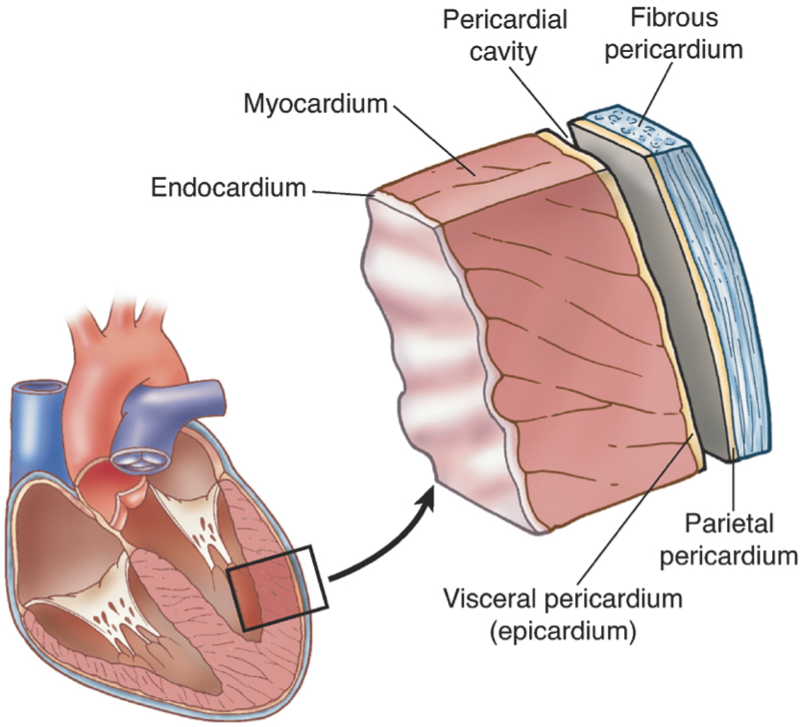
Cardiac muscle (or myocardium) makes up the thick middle layer of the heart. It is one of three types of muscle in the body, along with skeletal and smooth muscle. The myocardium is surrounded by a thin outer layer called the epicardium (AKA visceral pericardium) and an inner endocardium. Coronary arteries supply to the cardiac muscle, and cardiac veins drain this blood. Cardiomyocytes are the.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13939/LNOsY5VQ7ADcaM1g9m5g_Cardiac_Muscle.png)
Cardiac muscle tissue histology Kenhub
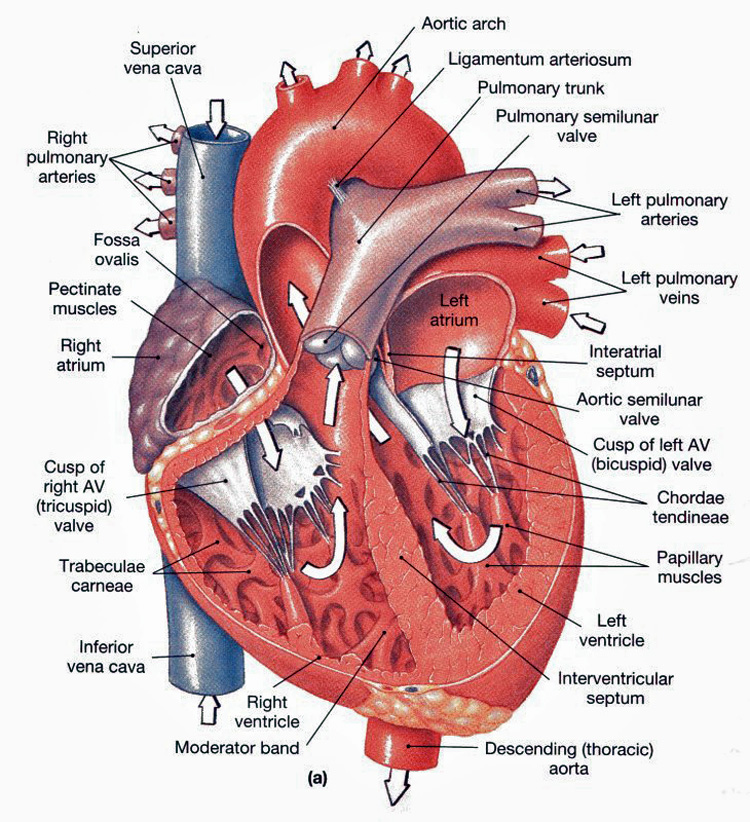
Heart anatomy. The heart has five surfaces: base (posterior), diaphragmatic (inferior), sternocostal (anterior), and left and right pulmonary surfaces. It also has several margins: right, left, superior, and inferior: The right margin is the small section of the right atrium that extends between the superior and inferior vena cava .

Cardiac muscle characteristics, functions and location (preview
The heart muscle is the myocardium or middle layer of the heart walls. The myocardium is responsible for the contractile function of the cardiac pump. Composed of cardiomyocytes, the heart muscle has distinctive cellular and physiological features allowing it to generate force to maintain adequate tissue and organ perfusion throughout the entire body. Heart muscle makes up one of the earliest.
Life as a Medical Student Cardiac Physiology
The human heart is primarily comprised of four chambers. The two upper chambers are called the atria, the remaining two lower chambers are the ventricles. The right and left sides of the heart are separated by a muscle called the "septum.". Both sides work together to efficiently circulate the blood.

Cardiac Muscle Vector Illustration Diagram, Anatomical Scheme with
Cardiac Muscle Diagram. The cardiac muscle or the myocardium forms the musculature of the heart. These are striated and involuntary muscles that are supplied by autonomic nerve fibres. They form the middle layer of the heart wall and are composed of cardiac muscle fibres. The other two layers are the pericardium (outer layer) and the.

Simple Cardiac Muscle Cell Diagram bmptips
Cardiac Muscle Definition. Cardiac muscle, also known as heart muscle, is the layer of muscle tissue which lies between the endocardium and epicardium. These inner and outer layers of the heart, respectively, surround the cardiac muscle tissue and separate it from the blood and other organs. Cardiac muscle is made from sheets of cardiac muscle.
cardiac muscles properties morphology
The epicardium covers the heart, wraps around the roots of the great blood vessels, and adheres the heart wall to a protective sac. The middle layer is the myocardium. This strong muscle tissue powers the heart's pumping action. The innermost layer, the endocardium, lines the interior structures of the heart. 2.
PPT the Heart Muscle Cell ( Cardiac striated muscle ) PowerPoint
What are the parts of the heart's anatomy? The parts of your heart are like the parts of a house. Your heart has: Walls. Chambers (rooms). Valves (doors). Blood vessels (plumbing). Electrical conduction system (electricity). Heart walls. Your heart walls are the muscles that contract (squeeze) and relax to send blood throughout your body.
Which is the cardiac muscle layer of the heart? Socratic
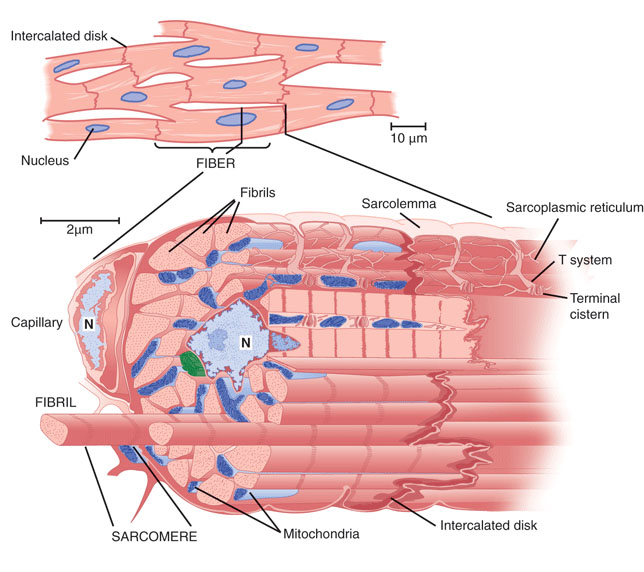
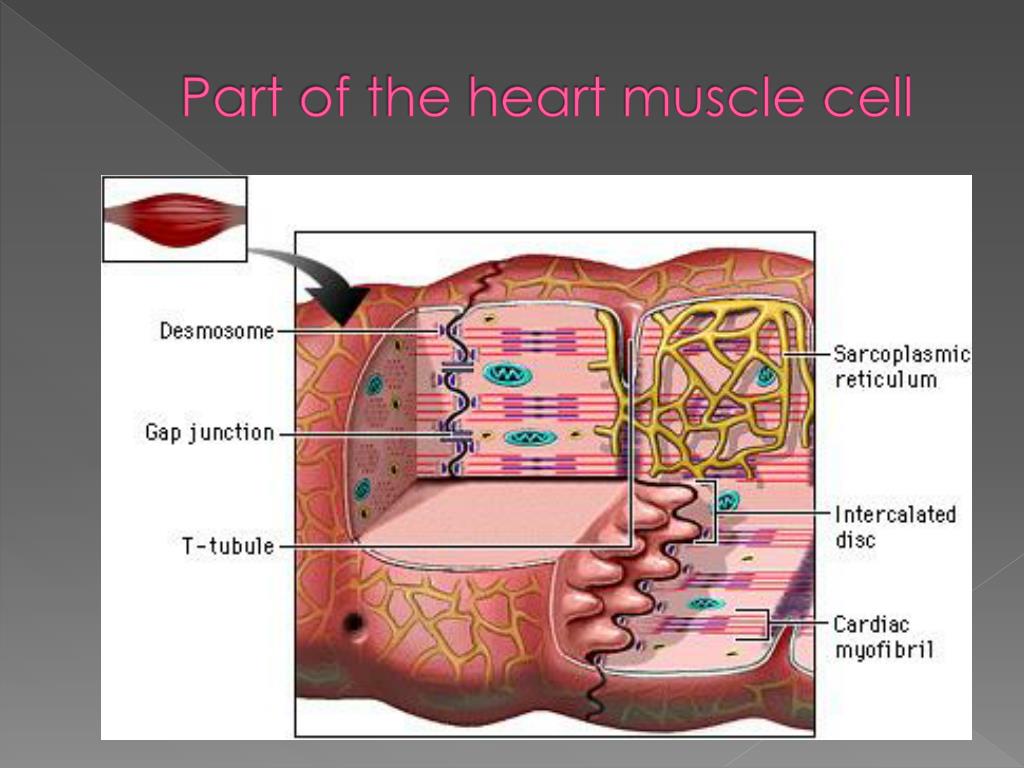
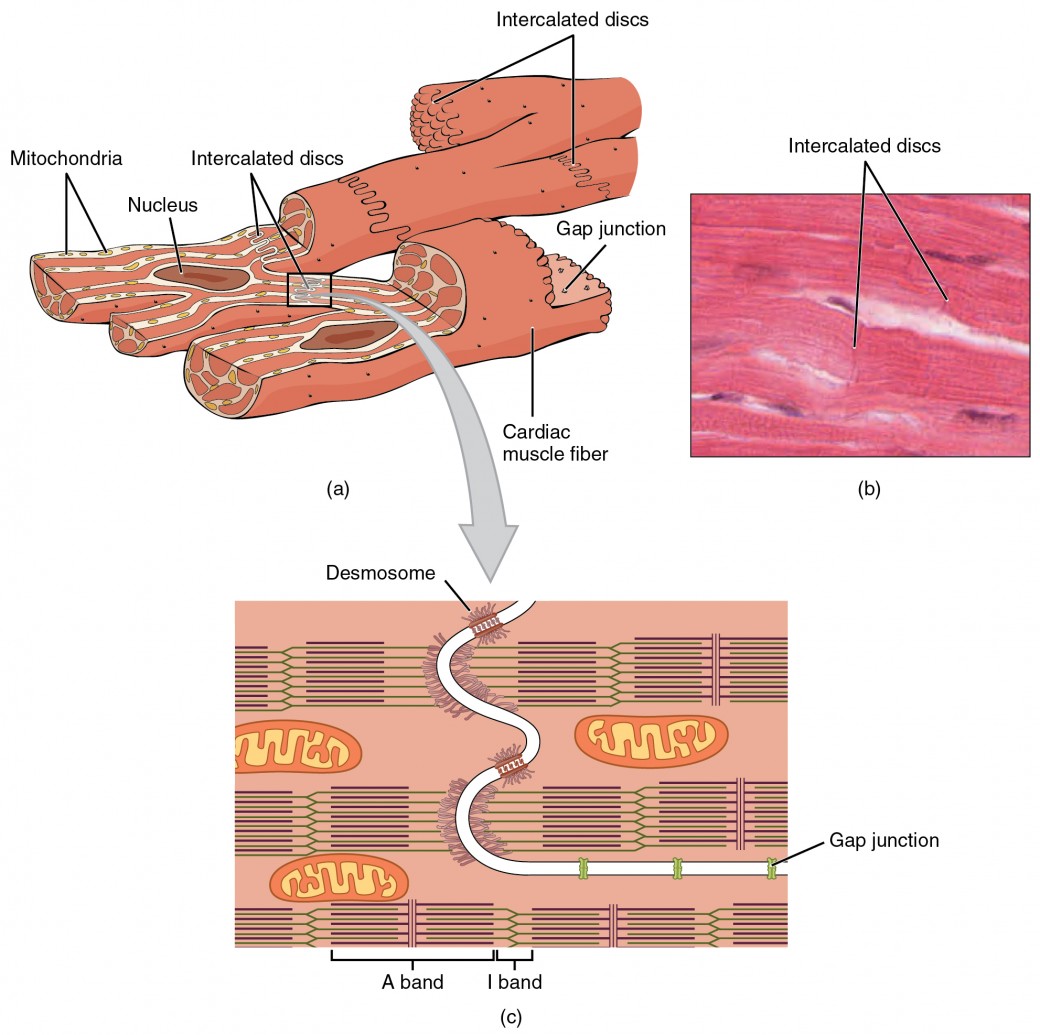
Cardiac muscle cells form a highly branched cellular network in the heart. They are connected end to end by intercalated disks and are organized into layers of myocardial tissue that are wrapped around the chambers of the heart. The contraction of individual cardiac muscle cells produces force and shortening in these bands of muscle, with a resultant decrease in the heart chamber size and the.
Cardiac Muscle and Electrical Activity Anatomy and Physiology II
Cardiac muscle tissue is one of the three types of muscle tissue in your body. It plays an important role in making your heart beat.. Use this interactive 3-D diagram to explore the movement of.

Structure of Cardiac Muscle Fibers. Anatomy of Cardiomyocyte Stock
Cardiac muscle cells ( cardiocytes or cardiac myocytes) make up the myocardium portion of the heart wall. The cardiac muscle cell or fiber. 1. 2. They are relatively short, branched fibers that measure approximately 10 to 10 micrometers in diameter and 50 to 100 micrometers in length. The cardiac muscle tissue consists of short branched fibers.

Labeled Cardiac Muscle koibana.info Heart structure, Heart function
So, the cardiac muscle under a microscope shows a short cylindrical fiber with a branch. The cardiac muscle fiber is made with cardiac myocytes, which contain centrally located single or multiple nuclei. All the provided labeled diagrams on cardiac muscle under a microscope might provide a clear idea.

Heart Anatomy · Anatomy and Physiology
Cardiac muscle tissue, also known as myocardium, is a structurally and functionally unique subtype of muscle tissue located in the heart, that actually has characteristics from both skeletal and muscle tissues.It is capable of strong, continuous, and rhythmic contractions that are automatically generated. The contractility can be altered by the autonomic nervous system and hormones.